|
|
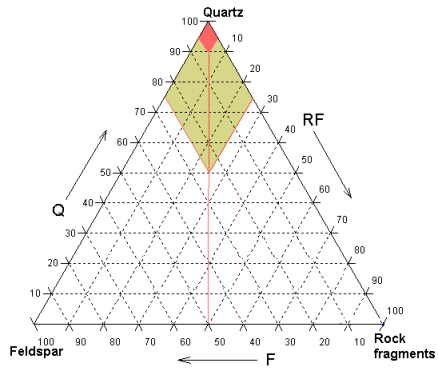
Framework
grains |
% |
||
|
# |
%Q |
%F |
%RF |
matrix |
|
A1 |
80 |
20 |
0 |
3 |
|
A2 |
85 |
10 |
5 |
6 |
|
A3 |
80 |
15 |
5 |
2 |
|
A4 |
85 |
15 |
0 |
3 |
|
A5 |
75 |
25 |
0 |
4 |
|
A6 |
75 |
20 |
5 |
2 |
|
A7 |
80 |
15 |
5 |
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B1 |
65 |
10 |
25 |
16 |
|
B2 |
60 |
15 |
25 |
17 |
|
B3 |
60 |
10 |
30 |
21 |
|
B4 |
65 |
5 |
30 |
14 |
|
B5 |
55 |
15 |
30 |
15 |
|
B6 |
55 |
10 |
35 |
22 |
|
B7 |
50 |
20 |
30 |
12 |
|
B8 |
50 |
10 |
40 |
18 |