Surfaces
GIS is capable of rendering 3D models. Two common structures are the raster grid and TIN (triangles).
Raster Surfaces - Can be conceived as a grid ‘bent into shape’.
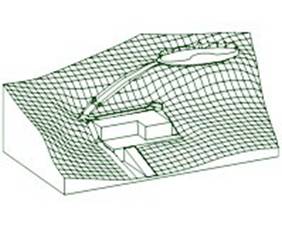
Terrain with buildings and road.
http://www.pracsys.hu/images/demo1_mesh.jpg
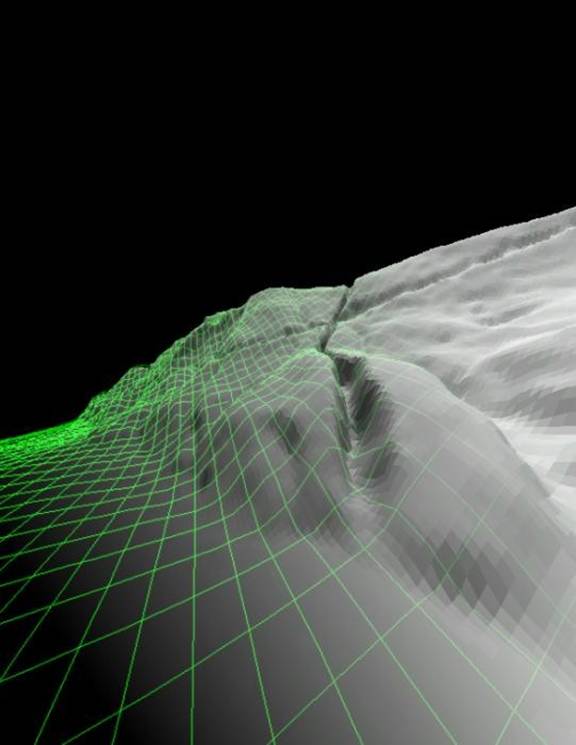
Surface showing the underlying 3D raster model.
http://www.geog.ucsb.edu/~jeff/projects/la_conchita/1995/eastgorge_wirestitch2.jpg
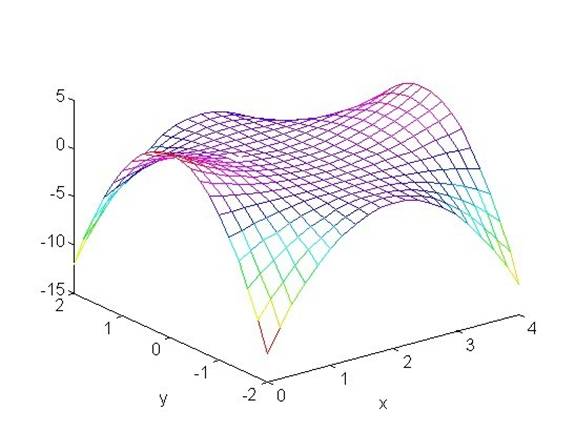
A wire mesh ‘bent’ into a 3-dimensional shape
http://oregonstate.edu/~peterseb/mth355/docs/surface_mesh.jpg
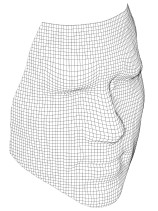
The shape of a face modeled with a ‘raster mesh’ – i.e. it doesn’t just have to be terrain that is modeled.
http://homes.esat.kuleuven.be/~spch/yearreports/1998/eamos.gif
TIN Surfaces – TIN = Triangulated Irregular Surface (any shape can be created from triangles, think of a geodesic dome)
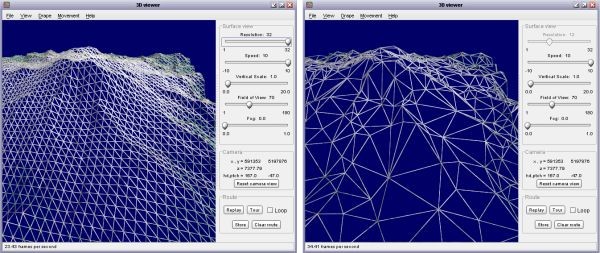
Terrain modeled with triangles (the left side has ‘regular sized’ triangles, while the right side has irregular sized triangles).
http://www.soi.city.ac.uk/~jwo/landserf/landserf220/doc/userguide/images/figure5.2.jpg

Face of the Statue of Liberty modeled with TIN
http://www.euclideanspace.com/threed/solidmodel/boundary/mesh/head2.gif
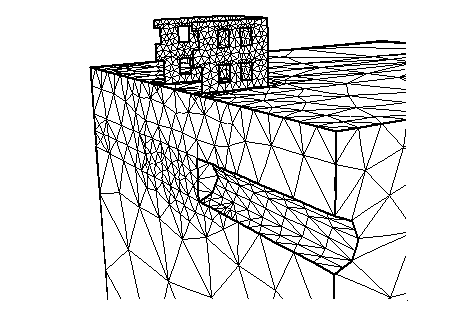
A ‘square’ fortress modeled with TIN.
http://www-civil.eng.ox.ac.uk/people/hjb/mesh.gif

A ‘new generation’ of TIN man.
http://www.unrealtechnology.com/screens/character_creation2.jpg
The next 3 images are of the USS Voyager
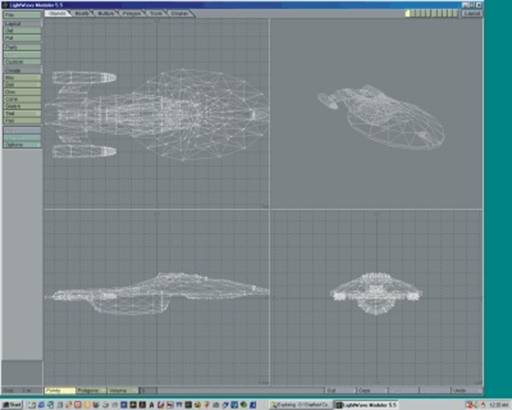
USS Voyager – underlying 3D model
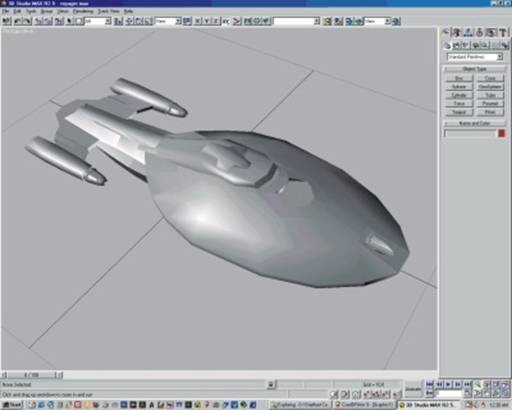
USS Voyager – with basic shading
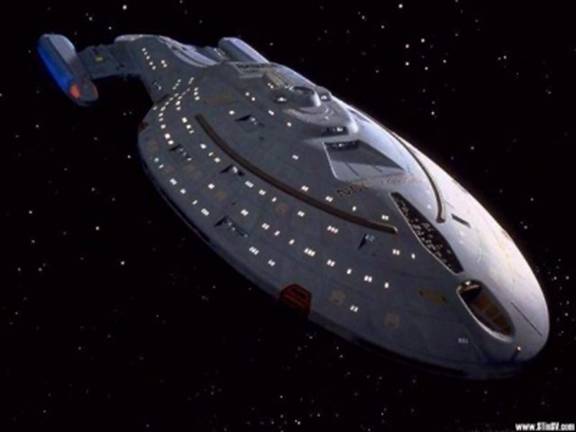

USS Voyager – after the computer artists have finished with it.